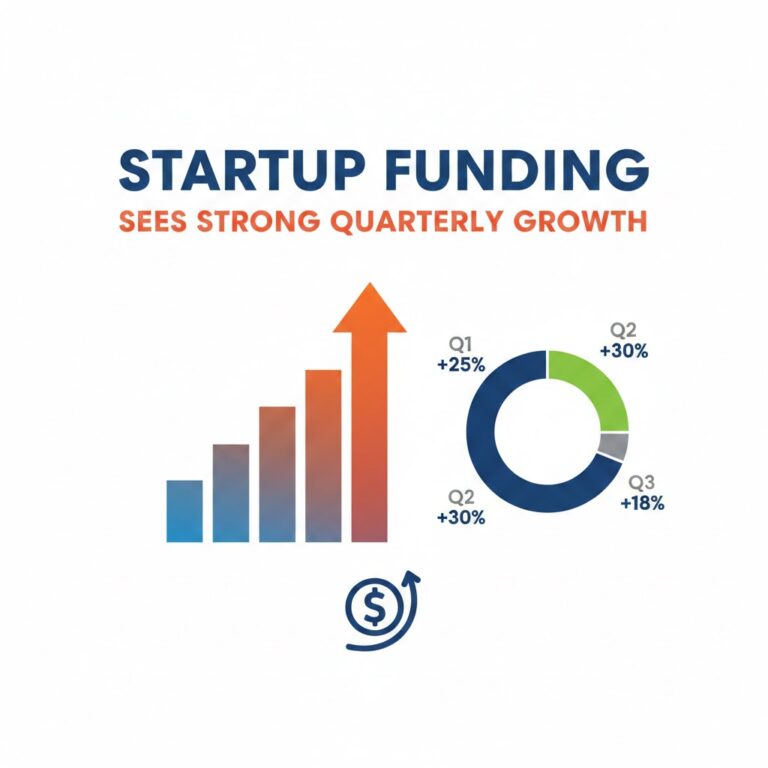
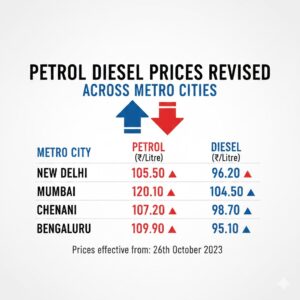
Cybersecurity has become one of the most critical priorities for businesses of all sizes. As digital transformation accelerates, cybercriminals are also becoming more organized, better funded, and more innovative. In 2025, businesses face a complex threat landscape where a single breach can disrupt operations, damage brand trust, and cause massive financial losses. This detailed guide explains the most serious cybersecurity threats companies must watch closely and prepare for in the year ahead, as regularly discussed by platforms like NewsTodayTak that track evolving digital risks.
The Rapid Evolution of Cyber Attacks
Cyber attacks are no longer random or opportunistic. Modern attackers conduct deep research on their targets, exploit human behavior, and use automation to scale attacks quickly. Businesses are now dealing with advanced persistent threats, multi-stage ransomware campaigns, and highly targeted social engineering tactics. The growth of cloud services, remote work, and connected devices has significantly expanded the attack surface, making traditional security models less effective.
AI-Powered Cybercrime
Artificial intelligence is being widely adopted by businesses, but cybercriminals are also using it to their advantage. AI-powered malware can adapt in real time, change its behavior to avoid detection, and identify system vulnerabilities faster than manual methods. Attackers are using AI to automate phishing campaigns, generate realistic fake emails, and even mimic executive communication styles. This makes it harder for employees and traditional security tools to detect malicious activity before damage occurs.
Ransomware Attacks Becoming More Destructive
Ransomware remains one of the most damaging cyber threats in 2025. Attackers are no longer just encrypting files; they are also stealing sensitive data and threatening to leak it publicly. This double-extortion model puts businesses under immense pressure to pay ransoms quickly. Industries such as healthcare, manufacturing, finance, and logistics are particularly vulnerable because system downtime can halt critical operations. Even companies with backups may still suffer reputational harm if customer data is exposed.
Supply Chain and Third-Party Vulnerabilities
Many businesses rely on third-party vendors, software providers, and cloud platforms. Cybercriminals increasingly target these supply chains because a single compromised vendor can provide access to hundreds of connected businesses. A security failure at a trusted partner can lead to widespread data breaches. Large technology ecosystems involving companies like Microsoft and Google have shown how deeply interconnected modern digital systems have become, making supply chain security a top concern.
Phishing and Social Engineering Attacks
Phishing remains one of the easiest and most effective attack methods. In 2025, phishing attacks are more personalized, more convincing, and harder to detect. Attackers use information from social media, data leaks, and AI-generated content to craft messages that look completely legitimate. Business email compromise attacks, where criminals impersonate executives or vendors, are increasing and often result in large financial losses. Employee awareness training alone is no longer enough without technical safeguards.
Cloud Security Misconfigurations
As more businesses move data and applications to the cloud, misconfigurations are becoming a major security risk. Poorly secured storage, weak access controls, and improper identity management can expose sensitive data to attackers. Many breaches are not caused by sophisticated hacking but by simple configuration errors. Cloud environments require continuous monitoring and specialized security practices, which many organizations still lack.
Internet of Things and Smart Device Risks
Connected devices are now common in offices, factories, and retail environments. From smart cameras to industrial sensors, the Internet of Things introduces thousands of new entry points for attackers. Many IoT devices have weak security, outdated firmware, or default passwords that are never changed. Once compromised, these devices can be used to spy on operations, launch internal attacks, or participate in large-scale botnets.
Insider Threats and Human Error
Not all cybersecurity threats come from outside the organization. Insider threats, whether malicious or accidental, remain a serious challenge. Employees may fall for phishing scams, reuse weak passwords, or mishandle sensitive data. Disgruntled staff or contractors with system access can intentionally cause harm. In 2025, businesses must focus on access control, activity monitoring, and a strong security culture to reduce insider-related risks.
Regulatory Pressure and Data Privacy Risks
Governments around the world are introducing stricter data protection and cybersecurity regulations. Failure to protect customer data can result in heavy fines, legal action, and long-term reputational damage. Businesses operating across multiple regions must navigate complex compliance requirements while maintaining consistent security standards. Data privacy failures are increasingly seen as corporate negligence rather than technical accidents.
Financial Impact of Cybersecurity Failures
The cost of cyber attacks continues to rise. Beyond ransom payments, businesses face legal fees, system recovery costs, lost productivity, and customer churn. Cyber insurance premiums are also increasing, and insurers are demanding stronger security controls before offering coverage. For small and mid-sized businesses, a single major breach can be enough to force permanent closure.
Preparing for Cybersecurity in 2025
To stay secure, businesses must adopt a proactive and layered security approach. This includes regular risk assessments, strong identity and access management, real-time threat monitoring, and incident response planning. Zero-trust security models are becoming essential, where no user or device is trusted by default. Continuous employee training, combined with advanced security tools, helps reduce both technical and human vulnerabilities.
Final Thoughts
Cybersecurity threats in 2025 are more sophisticated, persistent, and damaging than ever before. Businesses that treat cybersecurity as a core business strategy rather than a technical afterthought will be better positioned to survive and grow. Staying informed through reliable platforms such as NewsTodayTak and investing in long-term security resilience can help organizations protect their data, customers, and reputation in an increasingly digital world.